Well, it is June. I’ve been writing about technology all year (for the most part) and I hoped to have come to some conclusions by this time. All I know for sure is technology is here to stay, and I can hope we begin to use it, and implement it, thoughtfully. Or, for those who already do so, to continue thoughtful implementation.
Often I worry I’m making a bigger problem out of this than it really is. I mean, technology has always advanced over time and humans and societies adapt. But this technology seems to come with specific and deeply problematic long term issues both for cognitive and physical development of children. I tend to be affected by my environment in moderate ways. Therefore, too much screen time leaves me bleary and with headaches. I know this is not the case for everyone. Though this week, I’ve had two conversations leaving me confident that I’m not the only person with these concerns. My child’s ophthalmologist said that since the school district moved to 1:1 implementation, her office is selling more and more glasses to kids who do not have a stigmatism, but need glasses with blue light filters to prevent headaches from extended screen exposure.
I’ve also heard students discussing in class, hallways, and in their final papers how concerned they are about government, the environment, and society in general because they see their own generation as one so distracted and ignorant they feel no sense of hope for positive change. That seems dismaying. It seems a rite of passage to me for teenagers to feel their generation will improve on the faults and errors of the previous generation. To be misanthropic as a seventh grader or a junior in high school, seems problematic.
My juniors were given a final research paper under the theme, “the language of social media.” No one has a positive take on this theme. There are some balanced perspectives. My favorite phrase so far is, “the conundrum of constant connection,” read by a student who delivered her paper via reading it off of her phone. She stood before us and criticized the medium while utilizing it. A perfect visual of the benefit while presenting thoughtful questions of concern. Some have humorous explorations on how the language is used, or has changed. One student is writing a wonderful exploration of slang, and catch phrases. It is funny and engaging. Most are writing about how social media causes isolation, depression, a sense of time wasted, and—yes—a misanthropic view of the world.
I don’t really know how to help them. How does one change the larger habits of a society? Especially, pleasurable habits. Aldous Huxley and George Orwell keep being called upon in their papers. One student said, “if in Huxley’s day a citizen was handed a smartphone and told, ‘here, this will allow you to be in contact with anyone you want all the time, but will record everything and monitor your location—the citizen would decline in a split second.’” These students seem convinced we are the frog, in the kettle, the stove on, and the water warming without our awareness. But they also seem to feel, that there are some frogs who know the water is warming and are fine with it. And some who feel the pot’s sides are so steep, escape is impossible. Though there are some resisting this. Some are grabbing on to Clay Shirkey’s wonderful ideas about accepting everything from the internet. We get amazing things (Wikipedia, genius, go fund me, kickstarter, improved research abilities, citizen reporting from previously closed societies, etc.). This is just our cultural moment.
I want to offer them hope, because I believe it is possible. The hope comes from them. From people. From our ability to stop, look at someone we are working with and to see them. To see their humanity, despite differences of any kind. Hope comes from the “civil conversations,” of Krista Tippet. Comes from the student who reads books in their spare time in classes, rather than hopping on social media. From the student who uses their phone mindfully as well as for distraction.
Last week, I participated in an international literary festival. I met writers from Greece, Ireland, New York, Florida, and Spain. We were a diverse group—different ages, languages, skin colors, sexual orientations, life experiences. By the end of the week, we were old friends, for the most part. Mutual respect, the ability to listen, and a focus on language brought us together. Now technology will keep us in touch, email, facebook, etc. I see these same qualities in many of my students. I hope I’ve cultivated their desire to engage with these things in their life now and in the future. That’s where my hope lies—there, and in the belief that they will see it within themselves and their peers in the not so distant future.


 On May 9th, Governor Inslee signed a
On May 9th, Governor Inslee signed a  It takes a little knowledge to dig a little deeper sometimes. This month, I am hitting the knowledge. Next month – I am digging a little deeper. What am I talking about? Character education! Let’s first get a little history…
It takes a little knowledge to dig a little deeper sometimes. This month, I am hitting the knowledge. Next month – I am digging a little deeper. What am I talking about? Character education! Let’s first get a little history…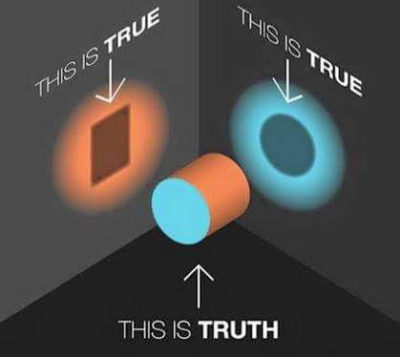 Which is truth?
Which is truth? We use a variety of terms to describe geographic areas in our school community. Upriver is a pretty common term used to describe the area due east of our community that parallels the Lewis River. I first heard this term when I started teaching in the district. When we received our first yearly snow, I was told that the kids who live upriver needed to go home. I didn’t really understand but later, during the summer, I went hiking and discovered that upriver includes a significant elevation gain that approaches the Gifford Pinchot National Forest and Mt. St. Helens. The bottoms is another area I’ve often heard students reference. I really had no sense of where that was nor did I ever find myself in a position to go explore the area. I’d ask and folks would point in a direction but it never made much sense to me. There was talk amongst staff that students would go hang out by the bottoms. I also knew that some of my students lived over there (wherever it was). I came to learn that this area is close to the Columbia River. There are a few parks down there and a road that runs along it that seems a bit too narrow for driving high speeds. It’s also host to some local farms and farm families.
We use a variety of terms to describe geographic areas in our school community. Upriver is a pretty common term used to describe the area due east of our community that parallels the Lewis River. I first heard this term when I started teaching in the district. When we received our first yearly snow, I was told that the kids who live upriver needed to go home. I didn’t really understand but later, during the summer, I went hiking and discovered that upriver includes a significant elevation gain that approaches the Gifford Pinchot National Forest and Mt. St. Helens. The bottoms is another area I’ve often heard students reference. I really had no sense of where that was nor did I ever find myself in a position to go explore the area. I’d ask and folks would point in a direction but it never made much sense to me. There was talk amongst staff that students would go hang out by the bottoms. I also knew that some of my students lived over there (wherever it was). I came to learn that this area is close to the Columbia River. There are a few parks down there and a road that runs along it that seems a bit too narrow for driving high speeds. It’s also host to some local farms and farm families.